Do you have a lump or pain in the testicle and are worried? Here is information on what could be and what are the guidelines that the doctor continues to find out.
Trauma
Shock or trauma are the most common injuries in children and causes usually mild to moderate pain. An ultrasound may see the hematoma and, in severe cases, bleeding. Usually it resolved with anti-inflammatory and analgesic.
Inguinal hernia
Uncomplicated inguinal hernias usually have the characteristic of reducibility (appear and disappear by pressing) which facilitates the diagnostic. It are painless mass penetrating from the abdomen is. If there is abdominal tissue (intestine) in the hernia, it must be operated quickly to avoid the lack of blood supply and death of the affected tissue.
Hydrocele
A hydrocele is the accumulation of fluid between the skin of the scrotum and testicle and presents as a painless scrotal mass. The swelling may be small in the morning, but becomes worse throughout the day, with large accumulations of fluid and heaviness, afternoon or evening. There is a nagging feeling of important unilateral weight. The diagnosis is relatively easy by palpation and transillumination of the scrotum. The ultrasound will confirm the diagnosis. Usually requires surgical treatment.
Varicocele
Varicocele is the presence of dilated veins in the testicles. Most varicoceles occur on the left side because the left testicular vein has a more vertical path and makes their work harder to pump blood into the left renal vein, which is where it ends. The varicocele is seen as a mass wormy back and above the testicles. Dilatation of the veins is reduced when the person is cast. Conversely, when most visible are these dilated veins is when the person is standing. The main problem that can give a varicocele is infertility. Not all varicoceles are associated with infertility, and not all require correction. The presence of an abnormal semen analysis in patients with clinically detectable varicocele should be treated, usually by microsurgery. Some varicoceles are causing a dull pain or heavy feeling, and this is also an indication for its removal by microsurgery. Microsurgery is similar to varicose vein surgery: dilated testicular veins are closed, either by surgical ligation or by injecting a liquid. Sometimes a varicocele is just notice something more important. Sometimes the blood circulation in the testicular veins is difficult because there is an obstacle in any area above. So, any sudden appearance of a varicocele on the left side of an older man should prompt the physician to investigate any problems in the kidney obstructing the testicular vein up to the kidney. Similarly, if there is a varicocele on the right side, the physician should rule out any possible obstruction of the vena cava.
A spermatocele is a painless cyst on the top and back of the testicles, which can move freely. Spermatocele is a kind of blind sac where sperm accumulates. When contents were examined, usually appear dead sperm. No treatment is needed unless the mass is annoying.
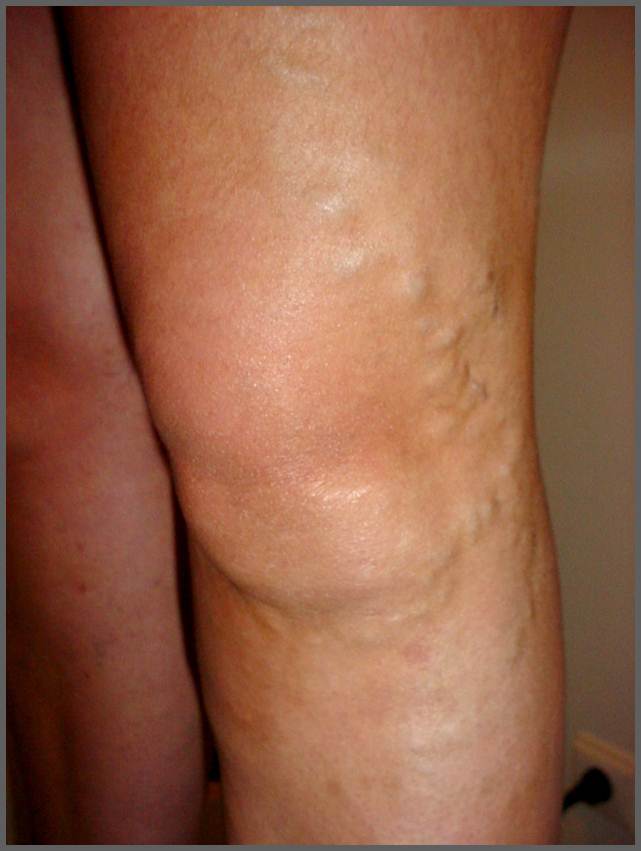 |
| The varicocele looks the same wormy varicose veins of the legs. You could say that the varicocele is a varicose vein in the testicle. |
Spermatocele
A spermatocele is a painless cyst on the top and back of the testicles, which can move freely. Spermatocele is a kind of blind sac where sperm accumulates. When contents were examined, usually appear dead sperm. No treatment is needed unless the mass is annoying.
Acute epididymitis
Epididymitis is the inflammation of the epididymis. The epididymis are two canals that cross outside the testes from top to bottom and can be easily felt. Its mission is to transport sperm to the ejaculatory duct. It sometimes happens that become infected. In fact, epididymitis is the most common cause of painful swelling of the testicles in males after puberty. The symptoms raising suspicion of epididymitis are gradual development of scrotal pain, fever, urethral discharge and urinary symptoms. On palpation, the epididymis causes pain and may be enlarged and hardened. It is very common the presence of pus in the urine.
The microorganisms that cause epididymitis are usually chlamydia, coliforms (E. coli, Klesbsiella, Proteus, Pseudomonas) and gonococcal infections (gonorrhea).
The (non-infectious) congestive epididymitis can occur after trauma to the epididymis and after surgical manipulations of the spermatic cord or vas deferens (herniorrhaphy, vasectomy, variocelectomia etc).
 |
| Epididymis in red |
The microorganisms that cause epididymitis are usually chlamydia, coliforms (E. coli, Klesbsiella, Proteus, Pseudomonas) and gonococcal infections (gonorrhea).
The (non-infectious) congestive epididymitis can occur after trauma to the epididymis and after surgical manipulations of the spermatic cord or vas deferens (herniorrhaphy, vasectomy, variocelectomia etc).
Testicular abscess
Is an undesired complication of orchitis. Pus-filled abscesses occur as a result of untreated bacterial infection. The symptoms are very apparent with severe testicular pain and swelling, loss of boundaries between the testis and epididymis, hydrocele fever and local inflammatory signs. Untreated cases tend adesarrollo purulent scrotal fistula. Testicular abscess should be treated by orchiectomy.
This is one of rotation on its axis testes (spermatic cord) so that the blood supply is cut. It is a serious and urgent case: should be operated quickly. It appears as a sharp pain in the testicular area. Physical examination shows testicles displaced from its correct position.The definitive diagnosis must be made by ultrasound and surgical treatment. If blood flow within six hours of torsion is restored, 80 to 100 percent of the testicles can be saved.Rates salvation of the testis down to 20 percent if the surgery is performed after more than 24 hours of scrotal pain.
Tumors
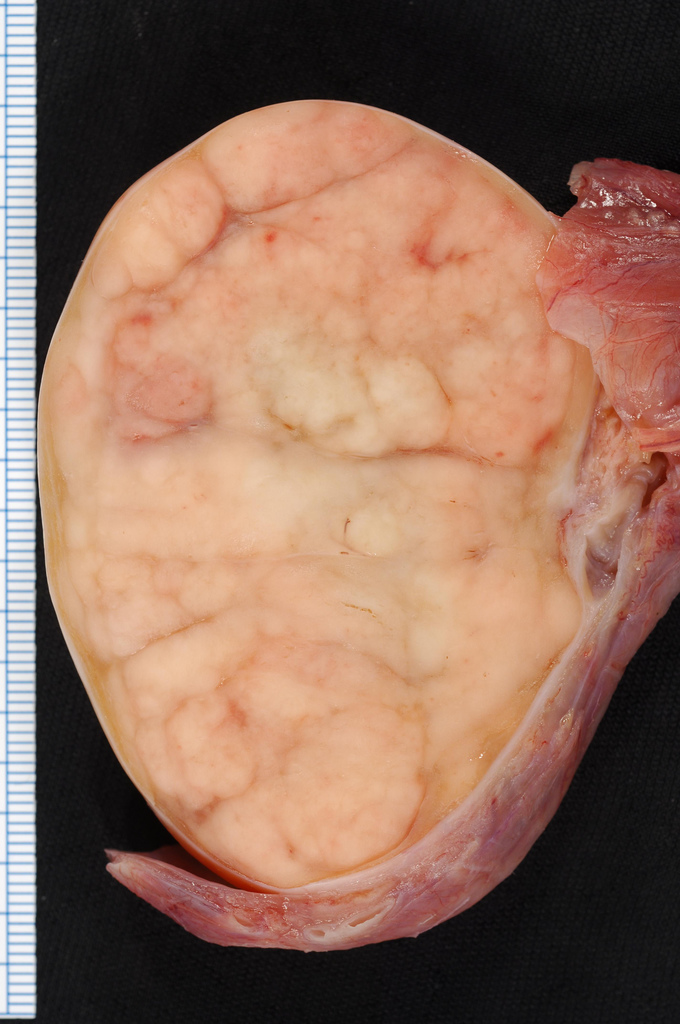
Malignant tumors of the testis are the most common cancer in individuals aged between 15 and 35 years.The testicular germ cell tumor is divided into two groups, according to the biological behavior of the injury, seminomas and non-seminomas . Seminomas, representing approximately 45% of cases are presented as solid lesions of regular and well-defined contours on ultrasound. Nonseminomas tumors, including embryonic carcinoma, teratocarcinomas, teratomas, choriocarcinomas and have a less uniform appearance with cystic areas, necrosis, calcifications and texture numerous terms desigual.En gonadal stromal tumors are usually benign and correspond to the Sertoli cell tumors and Leydig cells. Testicular tumors usually have an insidious onset and are rarely painful.
Seminoma
|
Lymphoproliferative disorders
Testicular lymphoma usually affects people over 50 years. A common feature is that it is usually bilateral. The testicles appear enlarged on ultrasound and an overall softer image is observed (hypoechoic)
Paratesticular tumors
Identification of solid lesions in the spermatic cord is clinically important because the prognosis is clearly related to a quick surgery and complete resection.
Finally, it is important that you go to the doctor. Faced with a lump in the testicle are many that let valuable time. Many men delay the visit to the doctor because they do not recognize the signs and symptoms, fear appearing weak, hypochondriacs, or lacking in masculinity. Others are embarrassed, fear the consequences of treatment or lack the time to consult their doctors. This only causes delays in diagnosis and treatment, we must not forget that after the first visit, we will suffer the inclusion in a list of incredibly slow wait. So the sooner the better.
Finally, it is important that you go to the doctor. Faced with a lump in the testicle are many that let valuable time. Many men delay the visit to the doctor because they do not recognize the signs and symptoms, fear appearing weak, hypochondriacs, or lacking in masculinity. Others are embarrassed, fear the consequences of treatment or lack the time to consult their doctors. This only causes delays in diagnosis and treatment, we must not forget that after the first visit, we will suffer the inclusion in a list of incredibly slow wait. So the sooner the better.